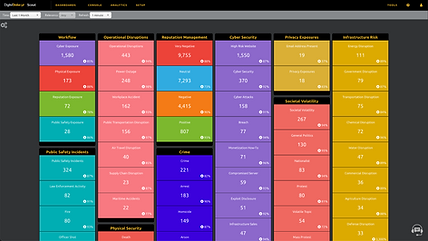
Environmental Risk Taxonomy for Environmental Intelligence
Overview of Environmental Intelligence
Environmental Intelligence involves the collection, analysis, and dissemination of information related to environmental threats, natural disasters, and climate-related risks that can impact organizations, communities, and ecosystems. This discipline is crucial for protecting against and mitigating the effects of environmental hazards and promoting sustainable practices.
Components of Environmental Intelligence
Environmental Threat Assessment
This component focuses on identifying and analyzing potential environmental threats, including natural disasters, climate change impacts, and human-induced environmental hazards.
Vulnerability Analysis
Vulnerability analysis involves assessing the susceptibility of infrastructure, communities, and ecosystems to environmental risks and identifying areas for resilience-building.
Sustainability and Mitigation Strategies
This aspect develops and implements strategies to reduce environmental risks, promote sustainable practices, and enhance resilience to environmental threats.
Importance of Environmental Intelligence
Environmental Intelligence is vital because it:
1. Protects Lives and Assets
Environmental intelligence helps safeguard:
Human lives from natural disasters and environmental hazards
Critical infrastructure from environmental damage
Natural resources and ecosystems
2. Enables Proactive Risk Mitigation
By providing early warning of potential environmental threats, it allows organizations to:
Implement preventive measures against natural disasters
Develop climate adaptation strategies
Adjust operations based on environmental forecasts
3. Enhances Organizational and Community Resilience
Environmental intelligence contributes to resilience by:
Informing disaster preparedness and response plans
Guiding sustainable development practices
Supporting continuous improvement of environmental management
4. Supports Regulatory Compliance
Environmental intelligence helps organizations:
Meet environmental protection regulations
Demonstrate commitment to sustainability
Prepare for and respond to environmental audits effectively
5. Ensures Business Continuity and Sustainability
By helping prevent and mitigate environmental incidents, this intelligence supports:
Uninterrupted business operations in the face of environmental challenges
Long-term sustainability of operations and resources
Maintenance of stakeholder trust through responsible environmental practices
Sample Environmental Event Types/Descriptions
1. Earthquakes
Seismic events that can cause:
Structural damage to buildings and infrastructure
Disruption of utilities and services
Potential for secondary hazards like tsunamis or landslides
2. Flooding
Inundation of normally dry land, leading to:
Property damage and loss
Disruption of transportation and communication networks
Potential health hazards and displacement of populations
3. Wildfires
Uncontrolled fires in natural areas, resulting in:
Destruction of property and natural habitats
Air quality issues and health risks
Disruption of local economies and ecosystems
4. Severe Storms
Intense weather events including hurricanes, tornadoes, and blizzards, causing:
Widespread damage to infrastructure
Power outages and communication disruptions
Potential for flooding and other secondary hazards
5. Environmental Contamination
Release of harmful substances into the environment, leading to:
Health risks for local populations
Damage to ecosystems and wildlife
Long-term environmental and economic impacts
Sample Environmental Article Titles
"Breaking: Magnitude 7.5 Earthquake Strikes Major Metropolitan Area, Widespread Damage Reported"
"Record-Breaking Heatwave Sparks Massive Wildfires Across Multiple States"
"Category 5 Hurricane Approaches: Coastal Cities Brace for Potentially Catastrophic Impact"
"Toxic Chemical Spill in Major River Threatens Water Supply for Millions"
"Global Climate Report Warns of Accelerating Sea Level Rise, Threatening Coastal Infrastructure"
Sample Courses of Environmental Action/Recommendations
1. Immediate Disaster Response
Activate emergency response protocols
Coordinate with local authorities and first responders
Implement evacuation procedures if necessary
2. Rapid Damage Assessment
Conduct swift assessments of affected areas
Prioritize critical infrastructure and life-saving operations
Mobilize resources for immediate relief and recovery efforts
3. Environmental Impact Mitigation
Implement containment measures for environmental contaminations
Assess and address immediate environmental threats
Develop long-term environmental remediation plans
4. Climate Resilience Planning
Develop and implement climate adaptation strategies
Enhance infrastructure resilience against environmental threats
Invest in sustainable technologies and practices
5. Stakeholder Communication and Engagement
Initiate crisis communication plans
Provide regular updates to affected communities and stakeholders
Engage in transparent reporting of environmental impacts and mitigation efforts